broadcast vs multicast vs unicast|unicast vs multicast vs broadcast vs anycast : Manila Broadcasting transfer (one-to-all) techniques can be classified into two types: Limited Broadcasting: Suppose you have to send a stream of packets to all the devices over the network that your reside, this broadcasting comes in handy. For this to . Tingnan ang higit pa TERMS OF USE. Welcome to QC eServices!. This e-Services Agreement (“Agreement”) is a legal agreement for the use of the software systems for the input, monitoring, validation, processing, and analytics of data (“Services”) between QC eServices (“us”, our”, or “we”) and the entity or person (“you”, “your”, or “user”) who registered on the QC eServices .
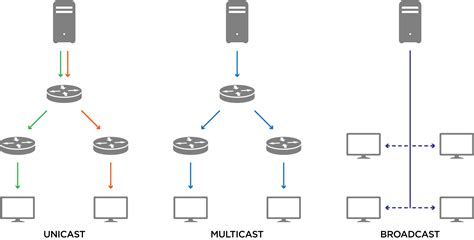
broadcast vs multicast vs unicast,In multicasting, one/more senders and one/more recipients participate in data transfer traffic. In this method traffic recline between the boundaries of unicast (one-to-one) and broadcast (one-to-all). Multicast lets servers direct single copies of data streams that are then simulated and routed to hosts . Tingnan ang higit pa
This type of information transfer is useful when there is a participation of a single sender and a single recipient. So, in short, you can term it a one-to-one transmission. For example, if a device having IP address 10.1.2.0 in a network wants to send the traffic . Tingnan ang higit pa
unicast vs multicast vs broadcast vs anycastThis type of information transfer is useful when there is a participation of a single sender and a single recipient. So, in short, you can term it a one-to-one transmission. For example, if a device having IP address 10.1.2.0 in a network wants to send the traffic . Tingnan ang higit pa
Broadcasting transfer (one-to-all) techniques can be classified into two types: Limited Broadcasting: Suppose you have to send a stream of packets to all the devices over the network that your reside, this broadcasting comes in handy. For this to . Tingnan ang higit pa Multicasting addresses messages for a specific group of devices in a network. Note that, even if a group contains all the devices in a network, multicast is theoretically different from the broadcast. .
Unicast communication is a one-to-one communication method, while broadcast is a one-to-all communication method. Unicast transmission is an .Multicast uses UDP (User Datagram Protocol) for “broadcasting” a stream over a closed IP network such as a LAN (Local Area Network) or an IP Service provider’s own . Broadcast and a Multicast are two different communication mechanism in computer networks for transmitting data between the .
The concept of Unicast and Multicast are same in IPv4 and IPv6, except the changes in IPv6 Layer 3 addresses used for broadcast & multicast and the Layer 2 address used .broadcast vs multicast vs unicast unicast vs multicast vs broadcast vs anycast Overview. Computer networks rely on various communication methods to transmit data between devices efficiently. Unicast, broadcast, and multicast are the .
A broadcast address represents all devices in the network. If a device want to share the information only with a single device, it uses the unicast address of that device. If a device want to share the information .
broadcast vs multicast vs unicast|unicast vs multicast vs broadcast vs anycast
PH0 · unicast vs multicast vs broadcast vs anycast
PH1 · multicast and unicast difference
PH2 · explain unicast multicast and broadcast
PH3 · difference between unicast and multicast
PH4 · difference between multicast and broadcast
PH5 · difference between broadcast and unicast
PH6 · difference between broadcast and multicast unicast
PH7 · define unicasting multicasting and broadcasting
PH8 · Iba pa